Home > Blogs > Endocrinology > Understanding the Difference Between Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
Understanding the Difference Between Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Each type has different causes, signs, and ways to manage it.
In this article, we’ll talk about what causes each type and the symptoms you might notice.
We’ll also explain how to manage both types of diabetes to keep your blood sugar levels under control and avoid any problems.
Föreställ dig en värld där striden mot impotens utkämpas med precisionen av ett fint inställt orkester. Tadalafil dirigerar den här symfonin och ser till att varje instrument i ensemblen spelar harmoniskt. Det är inte bara en tablett; det är dirigenten för din intima mästerverk. Köp Cialis och du är kompositören av din egen kärlekshistoria, där du skapar varje not med självförtroende och kraft.

Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
– Type 1 Diabetes
In type 1 diabetes, the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin, called beta cells. As a result, the body doesn’t make any insulin.
This type usually starts in childhood or adolescence, but it can also develop in adults.
People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump every day to replace the missing insulin and manage their blood sugar levels.
– Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is more common than type 1 and typically develops in adulthood. In this type, the body still produces insulin, but the cells don’t respond well to it, a condition known as insulin resistance.
Over time, the pancreas might not be able to produce enough insulin to overcome this resistance. Type 2 diabetes is often linked to factors like being overweight, having a sedentary lifestyle, and genetics.
It can usually be managed through a combination of healthy eating, exercise, weight loss, and sometimes medication or insulin therapy.
Causes & Symptoms of Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes
Causes and symptoms of type 1 and type 2 diabetes can differ significantly. Here’s an overview of each type:
– Type 1 Diabetes
Causes :
- The exact cause of type 1 diabetes is unknown, but it’s believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- It’s an autoimmune disease, meaning the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production.
Symptoms :
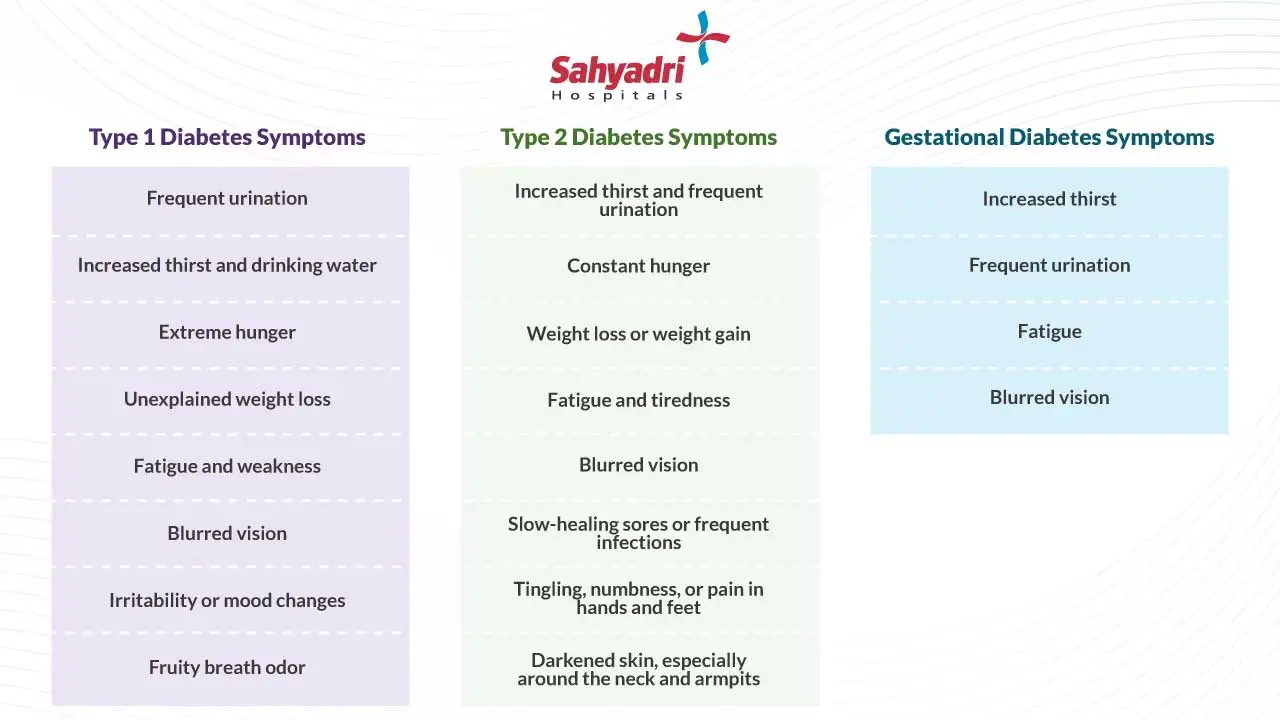
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Increased hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurry vision
- Irritability or mood change
Every diabetes patient have this question in their mind, Can diabetes be reversed or cured?
– Type 2 Diabetes
Causes :
- Type 2 diabetes develops when the body becomes resistant to insulin or the pancreas doesn’t produce enough insulin.
- Genetics: A family history of diabetes increases the risk.
- The risk increases as you get older, especially after age 45.
- Being overweight or obese raises the risk.
- A sedentary lifestyle with little physical activity contributes to insulin resistance.
- Consuming high amounts of sugar, unhealthy fats, and processed foods can increase the risk.
Symptoms :
Symptoms of type 2 diabetes can be similar to type 1 but may develop more gradually. They include:
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurry vision
- Slow-healing sores or cuts
- Frequent infections
- Tingling or numbness in hands or feet
It’s essential to recognize these symptoms and consult a diabetologist in Pune for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Early detection and management can help prevent complications and improve the quality of life for people with diabetes.
There is too much misinformation about diabetes among people. know these myths & facts about diabetes.
How Type 1 & Type 2 Diabetes are Managed?
Managing type 1 and type 2 diabetes involves different approaches, but the primary goal is to maintain healthy blood sugar levels and prevent complications.
Doctors advice for Management of diabetes for Type 1 & Type 2
– Insulin therapy :
Since the body doesn’t produce insulin in type 1 diabetes, people need to take insulin through injections or an insulin pump.
There are various types of insulin, such as rapid-acting, short-acting, and long-acting, which are used based on individual needs.
– Blood sugar monitoring :
Regularly checking blood sugar levels throughout the day helps adjust insulin doses and make informed decisions about food, exercise, and medication.
– Healthy eating :
Following a balanced diet, focusing on nutrient-dense foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help manage blood sugar levels.
– Physical activity :
Regular exercise helps the body use insulin more effectively and can lower blood sugar levels. It’s essential to monitor blood sugar before, during, and after exercise to prevent low blood sugar (hypoglycemia).
– Regular check-ups :
Routine medical appointments and lab tests help monitor overall health and detect any potential complications early.
– Medication :
Oral medications or non-insulin injectables may be prescribed to help the body use insulin more effectively or stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin. In some cases, insulin therapy may also be necessary.
Every diabetes patient needs to know these dangerous blood sugar levels.
FAQ’s
1. Which diabetes is more dangerous – type 1 or 2?
It’s difficult to say which type of diabetes is more dangerous, as both types can lead to severe complications if not managed properly.
The key to preventing complications in either type is maintaining good blood sugar control, following a healthy lifestyle, and working closely with healthcare professionals.
Each type presents unique challenges, but with proper management, individuals with both type 1 and type 2 diabetes can live healthy, fulfilling lives.
2. Can you have type 1 & 2 diabetes at the same time?
It’s highly unlikely for someone to have both type 1 and type 2 diabetes simultaneously.
While they share some similarities, they are distinct conditions with different causes.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease where the body destroys its own insulin-producing cells, while type 2 diabetes is primarily caused by insulin resistance.
However, it’s possible for someone initially diagnosed with type 2 diabetes to later develop an autoimmune response that destroys their remaining insulin-producing cells, resulting in a condition called latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA).
LADA shares features of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes but is still considered a separate condition.
3. What are the similarities between type 1 and 2 diabetes?
Both type 1 and type 2 diabetes share some similarities, which include:
- High blood sugar levels :
Both types result in elevated blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to use or produce insulin effectively.
- Symptoms :
Both types can have similar symptoms, such as frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, fatigue, blurry vision, and slow-healing sores or cuts.
- Complications :
If not managed properly, both types can lead to severe complications, including heart disease, kidney damage, nerve damage, eye problems, and foot problems.
- Management :
Both types require regular blood sugar monitoring, healthy eating, physical activity, and regular check-ups with healthcare professionals.
Takeaway
In summary, both type 1 and type 2 diabetes are chronic conditions characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce or use insulin effectively.
While they have different causes and management approaches, the primary goal for both types is maintaining healthy blood sugar levels and preventing complications.
Proper diabetes management involves regular blood sugar monitoring, healthy eating, physical activity, taking prescribed medications, and working closely with healthcare professionals.
By following this advice, individuals with diabetes can lead healthy, fulfilling lives.
Patient Feedback
Great doctors, Good facilities, caring and helping staff. I recommend this hospital for day care services.
![]()
![]()
Sangram Shinde
All doctors r very good. There treatments is best. Other staff also good. The service of nurses is great...Hospital is always clean.
![]()
![]()
Vaishali Aitawade
All services provide by hospital are nice and on time. Doctors are polite and co-operative with patient.
![]()
![]()
Ankita Jagtap
All services provided by hospital is good. Hygiene maintained well.Even at night good care provided.
![]()
![]()