Home > Blogs > Endocrinology > Diabetes Guide : Types, Symptoms, Treatments & more
Diabetes Guide : Types, Symptoms, Treatments & more
Navigating the world of diabetes can be overwhelming. Especially for those who are newly diagnosed.
In this article, we will explore the different types of diabetes, discuss the symptoms associated with each type, and provide an overview of treatment options.
Our goal is to empower you with knowledge, so you can better understand diabetes and confidently manage your health or support your loved ones on their journey.

Diabetes is a long-term health condition that affects how your body processes sugar.
When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t make enough of a hormone called insulin or can’t use it properly.
Insulin helps manage the amount of sugar in your blood, and when it doesn’t work right, it can lead to various health problems.
With millions of people affected by diabetes worldwide, it’s essential to know about the different types, their symptoms, and how to treat them.
Different Types of Diabetes & How They Affect the Body

There are 3 main types of diabetes. Type 1, Type 2, and gestational diabetes. Let’s take a closer look at each type and how they impact the body.
– Type 1 Diabetes
This form of diabetes, also known as juvenile diabetes, occurs when the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas.
As a result, the body cannot produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Type 1 diabetes usually develops in children and young adults but can occur at any age. People with this condition need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.
– Type 2 Diabetes
This is the most common form of diabetes, affecting about 90-95% of people with the condition.
In Type 2 diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or becomes resistant to it, causing blood sugar levels to rise. This type of diabetes is often linked to factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and genetic predisposition.
Over time, high blood sugar can damage blood vessels and nerves, leading to complications like heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and vision problems.
Lifestyle changes, oral medications, and sometimes insulin injections are used to manage Type 2 diabetes.
– Gestational Diabetes
This type of diabetes occurs during pregnancy when hormonal changes cause the body to become resistant to insulin. As a result, blood sugar levels can become elevated, potentially affecting both the mother and the baby.
Gestational diabetes usually resolves after giving birth, but women who have had it are at a higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes later in life.
Proper prenatal care, including monitoring blood sugar levels and making dietary adjustments, is crucial to managing gestational diabetes.
Understanding the different types of diabetes and how they affect the body is essential in managing the condition and preventing complications.
Every diabetes patient has to know these dangerous blood sugar levels to prevent further harm.
Symptoms of Type 1, Type 2 & Gestational Diabetes
The symptoms of diabetes can vary depending on the type, but there are some common signs that may indicate the presence of the condition.
Here are the symptoms associated with each type of diabetes:
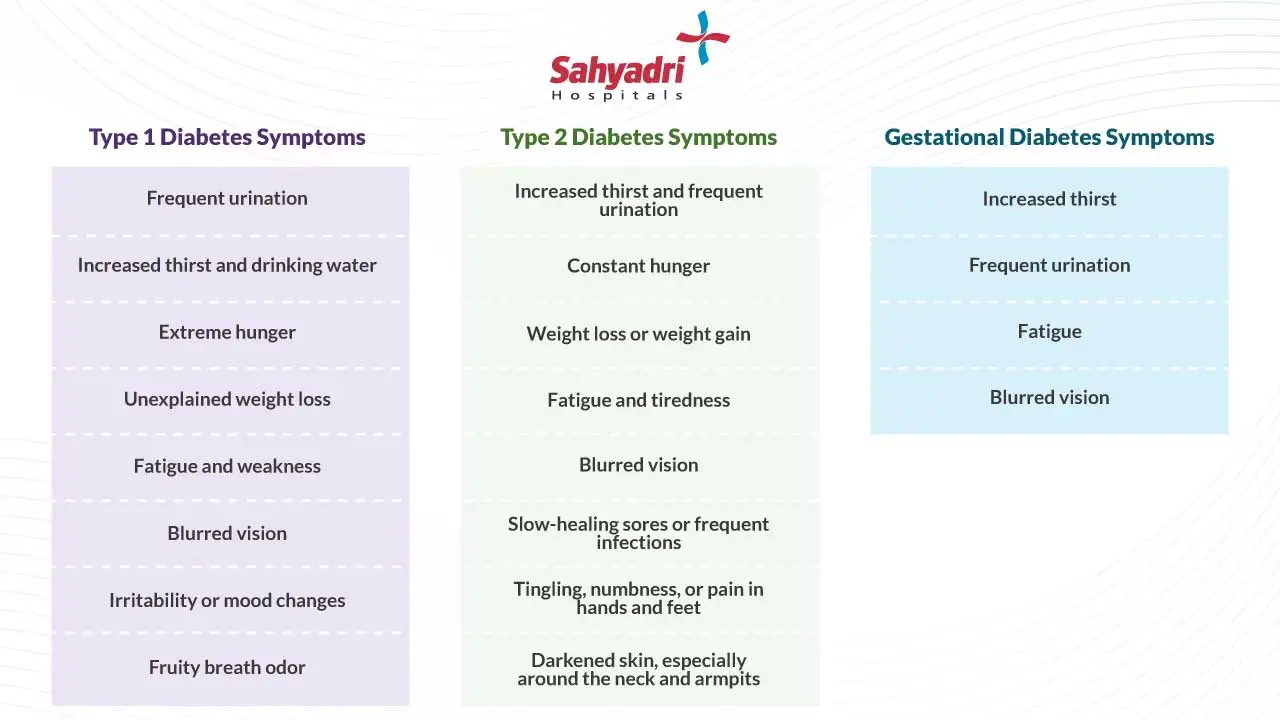
– Type 1 Diabetes Symptoms
- Frequent urination
- Increased thirst and drinking water
- Extreme hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue and weakness
- Blurred vision
- Irritability or mood changes
- Fruity breath odor
Do you want to know if diabetes is curable or not, click here to know facts about diabetes
– Type 2 Diabetes Symptoms
- Increased thirst and frequent urination
- Constant hunger
- Weight loss (despite eating more) or weight gain
- Fatigue and tiredness
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing sores or frequent infections
- Tingling, numbness, or pain in hands and feet (neuropathy)
- Darkened skin, especially around the neck and armpits (acanthosis nigricans)
– Gestational Diabetes Symptoms
Gestational diabetes often doesn’t show any noticeable symptoms, which is why it’s essential for pregnant women to undergo regular screenings.
However, some women may experience mild symptoms similar to those of Type 2 diabetes, such as:
- Increased thirst
- Frequent urination
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
It’s important to remember that these symptoms can also occur as a normal part of pregnancy, making it crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine if gestational diabetes is present.
If you or someone you know experiences any of these symptoms, it’s essential to consult a diabetologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Early detection and management of diabetes can help prevent complications and improve overall health.
Know these 5 safe fruits for diabetes patients.
Treatment Options for Each Type of Diabetes
Treatments used for different types of diabetes are mostly the same but treatments may vary depending on the type and severity of the condition.
The primary goal is to maintain blood sugar levels within a target range to prevent complications.
Here are the treatment options for diabetes:
– Insulin Therapy
Since the body doesn’t produce insulin in Type 1 diabetes, patients need to take insulin injections or use an insulin pump to regulate their blood sugar levels.
There are different types of insulin (rapid-acting, long-acting, etc.), and the healthcare provider will determine the most suitable one.
– Blood Sugar Monitoring
Regularly checking blood sugar levels is crucial for managing Type 1 diabetes. This helps adjust insulin doses and make necessary dietary or lifestyle changes.
– Carbohydrate Counting
Understanding the carbohydrate content of foods and adjusting insulin doses accordingly is essential for maintaining stable blood sugar levels.
– Oral Medications
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, doctors may prescribe oral medications that help the body use insulin more effectively or stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin.
Also, here is an interesting read about, Will diabetes unborn baby?
Takeaway
In conclusion, by understanding the complexities of each type and following personalized management plans, individuals can effectively manage their diabetes and prevent complications.
Collaborating closely with healthcare providers is essential for optimal health outcomes and living a healthy life with diabetes.
Patient Feedback
Great doctors, Good facilities, caring and helping staff. I recommend this hospital for day care services.
![]()
![]()
Sangram Shinde
All doctors r very good. There treatments is best. Other staff also good. The service of nurses is great...Hospital is always clean.
![]()
![]()
Vaishali Aitawade
All services provide by hospital are nice and on time. Doctors are polite and co-operative with patient.
![]()
![]()
Ankita Jagtap
All services provided by hospital is good. Hygiene maintained well.Even at night good care provided.
![]()
![]()